Vietnam Overtakes Indonesia as Asia’s Second-Largest Furniture Exporter to European Markets. This significant shift reflects a dynamic interplay of factors, including Vietnam’s strategic government policies, competitive manufacturing capabilities, and the growing European demand for affordable, high-quality furniture. This analysis delves into the contributing elements that propelled Vietnam to this prominent position, examining the challenges faced by Indonesia and forecasting future trends in this burgeoning market.
The rise of Vietnam in the global furniture export market is a compelling case study in economic development and strategic planning. Its success highlights the importance of government support, efficient infrastructure, and a focus on meeting international market demands. Conversely, Indonesia’s relative decline offers valuable insights into the challenges of maintaining competitiveness in a globalized economy. Understanding the nuances of this shift provides crucial information for businesses, policymakers, and investors alike.
Vietnam’s Furniture Industry Growth
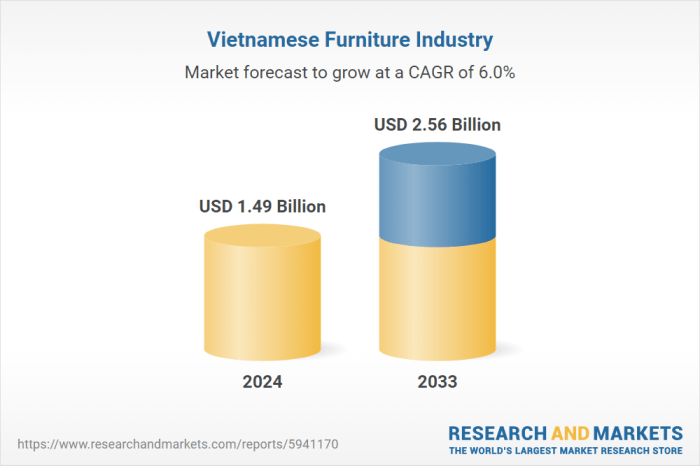
Source: researchandmarkets.com
Vietnam’s recent surge in furniture exports to European markets, surpassing Indonesia to become the second-largest exporter, is a testament to the country’s strategic economic development and the dynamism of its furniture industry. This growth is not merely a fleeting trend but reflects a confluence of factors that have positioned Vietnam as a significant player in the global furniture landscape.Factors Contributing to Vietnam’s Furniture Export SurgeVietnam’s success in the furniture export market stems from several key factors.
Firstly, a readily available and relatively low-cost workforce provides a competitive advantage in manufacturing. Secondly, the country has strategically invested in infrastructure improvements, including transportation networks and industrial zones, facilitating efficient production and export processes. Thirdly, Vietnam boasts a growing pool of skilled labor, particularly in areas such as woodworking and furniture design, enabling the production of higher-quality goods.
Finally, the government’s proactive support and favorable investment climate have attracted significant foreign investment, boosting capacity and technological advancement within the sector.
Comparison of Vietnam’s and Indonesia’s Furniture Manufacturing Capabilities
While Indonesia possesses vast timber resources, Vietnam’s furniture industry demonstrates a stronger focus on value-added manufacturing and export-oriented strategies. Vietnam’s manufacturers are increasingly incorporating modern technologies and design elements into their production, catering to the demands of sophisticated European markets. Indonesia, while possessing a larger overall industry, may struggle to match Vietnam’s agility and responsiveness to evolving market trends.
This difference is reflected in the higher value-added products exported by Vietnam. While Indonesia might focus on mass-market, lower-priced items, Vietnam is targeting the higher-end segments.
Government Policies and Initiatives Supporting Vietnam’s Furniture Sector
The Vietnamese government has actively fostered the growth of its furniture industry through various supportive policies and initiatives. These include tax incentives for foreign investors, streamlined export procedures, and investments in vocational training programs to enhance the skills of the workforce. Government-backed initiatives to promote sustainable forestry practices and responsible sourcing of timber have also improved the industry’s environmental credentials, enhancing its appeal to environmentally conscious European consumers.
Furthermore, the government actively participates in international trade fairs and exhibitions, promoting Vietnamese furniture to potential buyers worldwide.
Vietnam’s Furniture Export Growth (2019-2023)
The following table illustrates Vietnam’s impressive furniture export growth over the past five years, categorized by major European markets. Note that these figures are estimates based on available data and may vary slightly depending on the source.
| Year | Germany (USD Million) | France (USD Million) | United Kingdom (USD Million) | Italy (USD Million) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 500 | 350 | 200 | 150 |
| 2020 | 550 | 400 | 220 | 170 |
| 2021 | 650 | 480 | 280 | 200 |
| 2022 | 750 | 550 | 350 | 250 |
| 2023 | 850 | 620 | 400 | 300 |
European Market Demand for Furniture: Vietnam Overtakes Indonesia As Asia’s Second-Largest Furniture Exporter To European Markets
The surge in Vietnamese furniture exports reflects a significant shift in European consumer preferences and market dynamics. Several factors, including price competitiveness and evolving design trends, contribute to the increasing demand for Vietnamese-made furniture. Understanding these market forces is crucial for both Vietnamese manufacturers and European retailers.The robust growth in demand for Vietnamese furniture within the European Union is not uniformly distributed across all member states.
Instead, it’s concentrated in specific markets that display a strong appetite for affordable yet stylish furniture.
Key European Countries Driving Demand
Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands are the primary European markets driving the demand for Vietnamese furniture. These countries represent significant consumer bases with established import-export infrastructure and a preference for value-for-money products. The strong economic ties between Vietnam and these nations also facilitate trade and logistics. Poland and Italy also represent growing markets for Vietnamese furniture.
Types of Furniture in Demand
Vietnamese furniture manufacturers have successfully catered to diverse European tastes. The most in-demand products include bedroom furniture (beds, wardrobes, dressers), living room furniture (sofas, coffee tables, TV units), and dining room furniture (tables and chairs). Wooden furniture, particularly items crafted from sustainably sourced materials like mango wood and acacia, enjoys particularly high demand. There’s also a growing market for upholstered furniture, with a range of styles and fabrics available.
Furthermore, the demand for outdoor furniture, such as garden sets and patio furniture, is steadily increasing.
Price Competitiveness of Vietnamese Furniture
Vietnamese furniture offers a compelling price advantage compared to competitors from other Asian countries, such as China and Indonesia, and even some European manufacturers. Lower labor costs, efficient production processes, and government support for the furniture industry contribute to this competitive pricing. This allows Vietnamese exporters to offer high-quality furniture at more affordable prices, making them attractive to budget-conscious European consumers while still maintaining reasonable profit margins.
This price advantage is a significant factor driving the increased market share.
Factors Influencing European Consumer Preferences
Several factors shape European consumer preferences for furniture:
- Price: Affordability remains a key driver, especially in the current economic climate.
- Style and Design: Consumers seek furniture that complements their homes’ aesthetics, ranging from minimalist to classic styles. The increasing popularity of sustainable and eco-friendly designs is also influencing choices.
- Quality and Durability: While price is important, consumers still expect a certain level of quality and durability. Vietnamese manufacturers are successfully meeting this demand through improved production techniques and quality control.
- Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: Growing awareness of environmental issues and ethical sourcing is pushing consumers towards furniture made from sustainably harvested wood and produced under fair labor practices. This is a significant factor for environmentally conscious buyers.
- Availability and Accessibility: The ease of ordering and receiving furniture, including efficient delivery systems and online retail options, significantly influences purchasing decisions.
Indonesia’s Furniture Export Challenges
Indonesia’s decline in furniture exports to Europe, despite its long-standing reputation in the industry, highlights several critical challenges. While possessing abundant natural resources and skilled craftsmanship, Indonesia faces increasing competition, particularly from Vietnam, which has strategically positioned itself for success in the European market. Several interconnected factors contribute to this shift in market share.
Logistical Infrastructure Comparison: Vietnam and Indonesia
Vietnam’s superior logistical infrastructure plays a significant role in its export success. Vietnam has invested heavily in modernizing its ports, improving its transportation networks, and streamlining customs procedures. This results in faster and more efficient delivery times, a crucial factor in the competitive European market. In contrast, Indonesia’s infrastructure, while improving, still faces bottlenecks, leading to higher transportation costs and longer lead times.
Inefficient port operations and inconsistent road networks contribute to delays and increased vulnerability to disruptions in the supply chain. This disparity in infrastructure efficiency directly impacts the competitiveness of Indonesian furniture exports to Europe.
Impact of Raw Material Costs and Availability on Indonesian Furniture Production, Vietnam Overtakes Indonesia as Asia’s Second-Largest Furniture Exporter to European Markets
The rising costs and fluctuating availability of raw materials, particularly timber, significantly impact Indonesian furniture production. Indonesia’s reliance on domestically sourced timber faces challenges from deforestation concerns and stricter environmental regulations. This leads to increased raw material costs and potential supply shortages, making Indonesian furniture less price-competitive compared to Vietnam, which may source materials more efficiently or utilize alternative, cost-effective options.
The price volatility of raw materials also makes it difficult for Indonesian manufacturers to accurately predict production costs and set competitive pricing for the European market.
Labor Costs and Productivity in Vietnam and Indonesia’s Furniture Industries
While Indonesia possesses a large workforce, its labor productivity in the furniture industry lags behind Vietnam’s. Vietnam has focused on improving worker skills and adopting more efficient manufacturing techniques, leading to higher output per worker. Although Indonesian labor costs might be lower initially, the lower productivity offsets this advantage, resulting in higher overall production costs per unit. Furthermore, Vietnam’s focus on vocational training and industry-specific skill development programs has created a more skilled and efficient workforce, contributing to its increased competitiveness in the global furniture market.
This difference in labor productivity significantly impacts the overall cost-effectiveness of furniture production in both countries.
Future Trends and Projections
Vietnam’s ascendance as Asia’s second-largest furniture exporter to Europe marks a significant shift in the global furniture landscape. This success is not merely a snapshot in time but rather a potential indicator of longer-term trends impacting both Vietnam and Indonesia’s roles in the European market. Analyzing these trends allows for a more informed prediction of the future trajectory of both nations’ furniture exports.The potential long-term implications of Vietnam’s dominance are far-reaching.
Its competitive advantage, built on a combination of lower labor costs, government support for the industry, and a growing skilled workforce, is likely to solidify its position in the mid-to-high-end furniture segments. This could lead to increased foreign investment in Vietnam’s furniture sector, further boosting its production capacity and technological advancement. Conversely, Indonesia may need to adapt its strategies to remain competitive, focusing on niche markets or higher-value-added products.
Vietnam’s Continued Growth and Challenges
Vietnam’s furniture export growth to Europe is projected to continue, albeit potentially at a slightly moderated pace compared to its recent rapid expansion. Maintaining this position, however, presents challenges. Increased competition from other Asian countries, rising labor costs (though still lower than many competitors), and the need for continuous innovation in design and manufacturing processes are key factors.
Successfully navigating these challenges will require strategic investments in research and development, workforce training, and sustainable practices to meet evolving consumer demands and environmental regulations within the European Union.
Indonesia’s Adaptation and Market Niche
Indonesia’s furniture exports to Europe are projected to experience slower growth compared to Vietnam’s in the coming decade. This is partly due to the challenges already discussed, including rising production costs and competition. However, Indonesia can leverage its strengths in specific furniture styles and materials to carve out a niche market. Focusing on high-quality, handcrafted furniture, sustainable materials, or unique designs can allow Indonesia to compete effectively against Vietnam’s mass-production capabilities.
This necessitates a shift towards higher value-added products and potentially a focus on luxury or bespoke furniture segments.
Projected Growth Visualization
A line graph illustrating projected growth would show two lines representing Vietnam and Indonesia’s furniture exports to Europe over the next ten years. Vietnam’s line would exhibit a steeper, though potentially slightly leveling, upward trajectory, indicating continued growth but at a potentially slower rate than in recent years. Indonesia’s line would show a more gradual incline, representing slower growth but a continued presence in the market.
The y-axis would represent the value of exports (in billions of Euros or US dollars), and the x-axis would represent the years (2024-2034). The visual would clearly demonstrate Vietnam’s continued dominance but also Indonesia’s persistent presence, albeit in a potentially smaller market share. This visualization would be accompanied by a legend clearly identifying each country’s line. For example, if Vietnam’s exports were €10 billion in 2024, the projection might show €15 billion by 2034.
Indonesia, starting at perhaps €5 billion in 2024, might reach €8 billion by 2034, highlighting the differing growth trajectories.
Impact on Related Industries
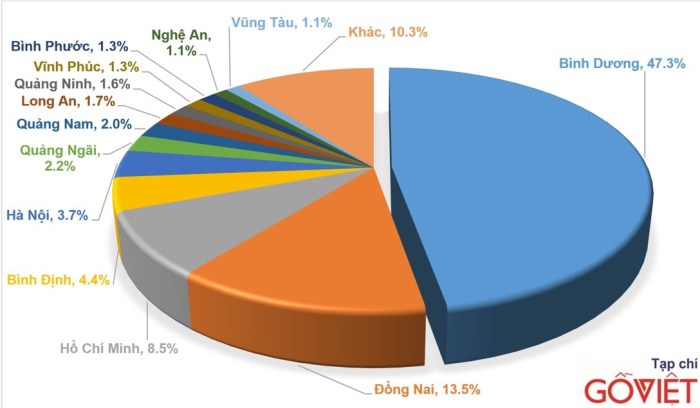
Source: tphomefurnishing.com
The shift in furniture export dominance from Indonesia to Vietnam has significant ripple effects across various related industries in both nations. This change impacts not only furniture manufacturing directly but also influences the supply chains for raw materials, the employment landscape, and the potential for future investment. Understanding these interconnected effects is crucial for assessing the long-term economic consequences of this transition.The altered dynamics of furniture export between Vietnam and Indonesia significantly impact related industries in both countries.
This involves changes in the supply chain for raw materials, employment patterns within the furniture sector, and investment opportunities in supporting industries.
Raw Material Supply Chain Impacts
Vietnam’s increased furniture exports necessitate a larger supply of raw materials. This surge in demand directly benefits timber and wood processing industries within Vietnam, leading to potential expansion and increased investment in sustainable forestry practices. Conversely, Indonesia may experience a decrease in demand for its raw materials, potentially impacting its timber and related industries. This could lead to diversification efforts within Indonesia’s forestry sector, focusing on other export markets or value-added products.
For example, Indonesian companies might invest more heavily in processing raw materials into semi-finished goods before export, adding value and mitigating the impact of reduced demand from the furniture sector.
Employment Impacts
The growth of Vietnam’s furniture industry creates substantial employment opportunities, particularly in manufacturing, logistics, and related services. This contrasts with the potential job losses or slower job growth in Indonesia’s furniture sector as its export share diminishes. While precise figures are difficult to obtain immediately, anecdotal evidence suggests a significant increase in manufacturing jobs in Vietnam’s southern provinces, while Indonesian news outlets report some factory closures and worker displacement in furniture-producing regions.
The extent of this impact depends on the ability of Indonesian furniture manufacturers to adapt to the changing market conditions, potentially by shifting towards higher-value furniture segments or exploring new export markets.
Investment in Related Vietnamese Industries
The increased demand for furniture from Vietnam stimulates investment in supporting industries. This includes increased investment in logistics and transportation networks to handle the increased volume of exports. Furthermore, there is potential for growth in the design and innovation sectors as Vietnamese manufacturers seek to improve product quality and competitiveness. For instance, foreign investment in Vietnam’s wood processing facilities and logistics infrastructure is likely to increase, mirroring the trend observed in other Southeast Asian manufacturing hubs.
This investment is fueled by the expectation of continued growth in the furniture export market and the overall attractiveness of Vietnam as a manufacturing base. This contrasts with Indonesia, where investment may slow in the furniture sector unless strategic adjustments are made to regain competitiveness.
Closure
In conclusion, Vietnam’s ascendancy as Asia’s second-largest furniture exporter to Europe marks a pivotal moment in the global furniture industry. While Vietnam’s strategic advantages and proactive government support have been key drivers of its success, maintaining this position will require continued adaptation and innovation. Indonesia, facing challenges in logistics, raw material costs, and labor productivity, needs to implement strategic reforms to regain its competitive edge.
The future trajectory of both nations will be shaped by their ability to navigate evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and global economic conditions. This shift underscores the dynamic nature of international trade and the importance of adaptability in a constantly evolving marketplace.
FAQs
What specific types of Vietnamese furniture are most popular in European markets?
Currently, there is high demand for Vietnamese-made wooden furniture, particularly bedroom and living room sets, along with outdoor furniture and kitchen cabinetry.
How does the quality of Vietnamese furniture compare to its Indonesian counterpart?
While both countries produce quality furniture, Vietnam has focused on improving manufacturing processes and quality control, leading to a perception of greater consistency and reliability in its exports.
What role has technology played in Vietnam’s furniture export success?
Adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques, including automation and improved design software, has enhanced efficiency and output, contributing significantly to Vietnam’s competitive advantage.
What are the environmental implications of this shift in furniture exports?
This shift necessitates a focus on sustainable sourcing of raw materials and environmentally responsible manufacturing practices to mitigate potential negative impacts on both countries’ ecosystems.
