Southeast Asian Furniture Exports Surge as Global Demand for Sustainable Materials Rises. This burgeoning market reflects a global shift towards eco-conscious consumption. Increasing awareness of environmental issues and a desire for ethically sourced products are driving demand for furniture crafted from sustainable materials like bamboo, rattan, and reclaimed wood. This trend presents significant opportunities for Southeast Asian nations, known for their skilled craftsmanship and abundant natural resources, to solidify their position as leading exporters in the global furniture industry.
The resulting economic benefits are substantial, impacting livelihoods and fostering sustainable development within the region.
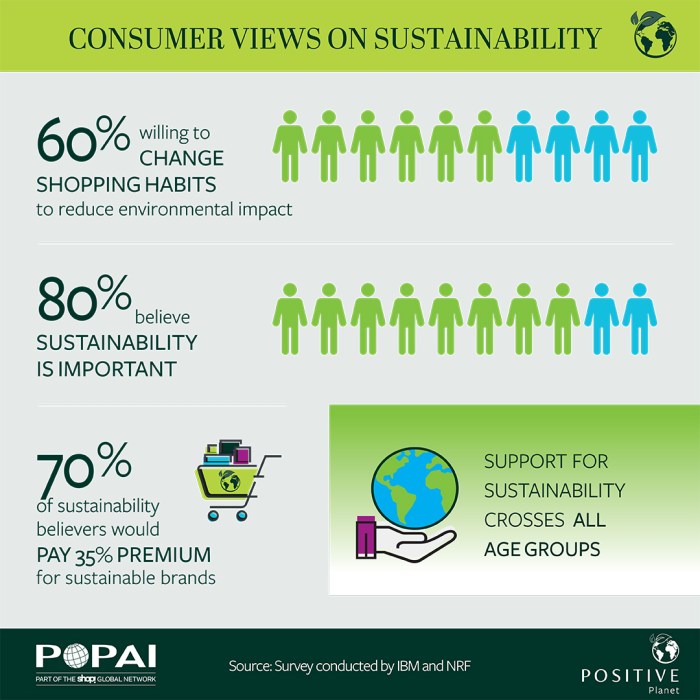
The rise in demand is not merely a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in consumer preferences. Consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for furniture made from sustainable materials, reflecting a growing commitment to environmental responsibility and social justice. This heightened awareness has created a lucrative market for Southeast Asian exporters, who are well-positioned to meet this demand with their readily available resources and established production capabilities.
This report will delve into the specifics of this surge, examining the key players, the challenges, and the exciting future prospects.
The Rise of Sustainable Materials in Global Furniture Demand
Source: wearepositive.com
The global furniture market is undergoing a significant shift, driven by a growing awareness of environmental concerns and a rising demand for ethically sourced products. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, leading to a surge in popularity for furniture crafted from eco-friendly and responsibly harvested materials. This trend is not merely a fleeting fashion but a fundamental change in consumer behavior reflecting a deeper commitment to environmental stewardship and social responsibility.The increasing global preference for sustainable and eco-friendly furniture is fueled by a confluence of environmental and social drivers.
Environmental concerns, such as deforestation, carbon emissions from manufacturing processes, and the disposal of furniture waste, are major factors. Consumers are becoming more educated about the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions and actively seeking out alternatives that minimize their carbon footprint. Simultaneously, social drivers, including fair labor practices and support for local communities, are influencing purchasing choices.
Consumers are increasingly interested in knowing where their furniture comes from and how it was made, preferring pieces produced with ethical considerations in mind. This translates to a stronger demand for transparency and traceability within the furniture supply chain.
Sustainable Materials Used in Southeast Asian Furniture
Southeast Asia, with its rich biodiversity and traditional craftsmanship, is well-positioned to capitalize on this global trend. The region boasts a wealth of sustainable materials readily adaptable to modern furniture design. The following table highlights some key examples:
| Material | Source Country | Sustainability Feature | Market Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bamboo | Vietnam, Indonesia, Philippines | Rapidly renewable, low carbon footprint, high strength-to-weight ratio | High and rapidly increasing, particularly for outdoor and contemporary styles. |
| Rattan | Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia | Sustainable harvesting practices are crucial; durable, lightweight, and versatile | Strong demand for handcrafted and woven furniture; increasing interest in modern interpretations. |
| Reclaimed Wood | Thailand, Myanmar, Laos | Reduces deforestation, gives character and unique aesthetic; requires careful sourcing and treatment | Growing demand for vintage and industrial styles; higher price point reflects unique nature of material. |
| Seagrass | Vietnam, Philippines | Naturally renewable, biodegradable, creates unique textures and patterns in furniture | Increasing demand for eco-friendly and natural-looking home décor. |
Types of Sustainable Furniture Exported from Southeast Asia: Southeast Asian Furniture Exports Surge As Global Demand For Sustainable Materials Rises
Southeast Asia is experiencing a surge in furniture exports, driven by the global shift towards sustainable and ethically sourced products. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a desire for furniture that reflects these values. The region’s diverse resources and skilled craftsmanship contribute significantly to this burgeoning industry, offering a wide range of sustainable furniture options for international markets.The types of sustainable furniture exported from Southeast Asia are diverse, catering to both residential and commercial needs, encompassing indoor and outdoor applications.
Design styles vary considerably, reflecting the rich cultural heritage of the region while incorporating modern aesthetics and sustainable material choices. The focus is increasingly on utilizing locally sourced, rapidly renewable materials and employing environmentally friendly production methods.
Categorization of Exported Furniture
Southeast Asian furniture exports span a broad spectrum of categories. Residential furniture constitutes a significant portion, encompassing living room sets, bedroom furniture, dining sets, and home office pieces. Commercial furniture, including pieces for restaurants, hotels, and offices, is also a growing sector. Outdoor furniture, crafted from weather-resistant materials, is another prominent category. These categories often overlap, with some pieces suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, depending on the materials and design.
Design Styles and Aesthetic Features
The design styles of sustainable furniture exported from Southeast Asia are incredibly varied. Traditional styles, reflecting the unique cultural heritage of each nation, are often incorporated. For instance, intricately carved teakwood furniture from Indonesia showcases traditional Javanese or Balinese motifs. Meanwhile, Vietnamese furniture may feature simpler, more minimalist designs with clean lines and a focus on functionality.
Modern interpretations of these traditional styles are also common, blending classic aesthetics with contemporary design sensibilities. Many pieces incorporate natural, earthy color palettes that complement the sustainable materials used in their construction.
Examples of Sustainable Furniture Pieces
The sustainable practices employed in Southeast Asian furniture manufacturing are often highlighted in the final product. Here are some examples:
- Teakwood Dining Table (Indonesia): Made from sustainably harvested teak, a durable hardwood known for its longevity and resistance to decay. The use of teak reduces the demand for less sustainable wood species. The table’s design may incorporate traditional Indonesian carving techniques, showcasing local craftsmanship.
- Bamboo Outdoor Chairs (Vietnam): Constructed from rapidly renewable bamboo, a sustainable and lightweight material ideal for outdoor use. The chairs’ simple, elegant design emphasizes the natural beauty of the bamboo, and the production process may involve minimal chemical treatments, minimizing environmental impact.
- Rattan Sofa Set (Philippines): This set showcases the versatility of rattan, a naturally strong and flexible vine. The sustainable harvesting and processing of rattan are crucial for its environmental viability. The sofa’s design might incorporate traditional Filipino weaving techniques, creating a unique and culturally significant piece.
- Recycled Rubberwood Bed Frame (Thailand): This demonstrates the potential of repurposing waste materials. Rubberwood, a byproduct of the rubber industry, is a sustainable alternative to traditional hardwoods. The bed frame’s design may incorporate modern aesthetics while utilizing the unique grain patterns of the recycled wood.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Southeast Asian Furniture Export Market
The surge in global demand for sustainable furniture presents both significant opportunities and considerable challenges for Southeast Asian furniture exporters. While the region possesses a wealth of resources and skilled craftsmanship, navigating the complexities of the international market requires strategic planning and adaptability. Success hinges on effectively addressing existing hurdles while proactively capitalizing on emerging trends.
Southeast Asian furniture exporters face a multifaceted landscape of challenges and opportunities. The competitive nature of the global market, coupled with logistical complexities and evolving trade policies, necessitates a proactive and strategic approach to ensure sustained growth and market share. Simultaneously, the increasing global preference for sustainable and ethically sourced products creates a powerful incentive for exporters to adopt eco-friendly practices and highlight their commitment to sustainability.
Challenges Faced by Southeast Asian Furniture Exporters
Several key challenges hinder the growth of Southeast Asian furniture exports. These challenges require careful consideration and strategic mitigation to ensure the continued success of the industry.
| Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Intense Competition from Other Regions (e.g., China, Vietnam): Southeast Asia faces stiff competition from established furniture manufacturing hubs with economies of scale and potentially lower labor costs. | Focus on niche markets and specialized products (e.g., handcrafted furniture, bespoke designs) to differentiate offerings. Invest in design innovation and superior craftsmanship to command premium prices. Develop strong brand identities and marketing strategies to build customer loyalty. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events (pandemics, geopolitical instability) and logistical bottlenecks can significantly disrupt the supply chain, impacting production timelines and delivery schedules. | Diversify sourcing of raw materials and establish multiple supply chain partners to mitigate risk. Invest in robust inventory management systems and explore alternative transportation routes. Build strong relationships with reliable logistics providers. |
| Trade Regulations and Tariffs: Navigating complex international trade regulations, tariffs, and import/export procedures can be costly and time-consuming. | Seek expert advice on international trade law and compliance. Develop strong relationships with customs brokers and trade representatives. Proactively monitor changes in trade policies and adapt strategies accordingly. |
| Maintaining Sustainable Practices: Balancing profitability with environmental sustainability and ethical sourcing can present operational challenges and increased costs. | Invest in sustainable forestry practices and utilize certified wood sources (e.g., FSC certification). Implement efficient waste management systems and reduce carbon emissions throughout the production process. Transparency in supply chains and ethical labor practices are crucial for building consumer trust. |
| Lack of Access to Finance and Technology: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often face challenges in accessing financing for expansion and upgrading technology. | Explore government support programs and microfinance initiatives designed to assist SMEs. Collaborate with technology providers to adopt efficient manufacturing processes and digital marketing strategies. Seek partnerships with larger companies to access resources and expertise. |
Opportunities Presented by Growing Global Demand for Sustainable Furniture
The increasing global awareness of environmental issues and the growing preference for sustainable products create significant opportunities for Southeast Asian furniture exporters. Capitalizing on this trend requires a strategic approach that leverages the region’s strengths and addresses its weaknesses.
The rising demand for sustainable furniture offers a compelling opportunity for Southeast Asian exporters to establish themselves as leaders in the global market. By emphasizing eco-friendly materials, ethical sourcing, and sustainable manufacturing practices, these exporters can attract environmentally conscious consumers willing to pay a premium for responsibly produced furniture. This presents a chance not only to increase market share but also to build a strong brand reputation associated with sustainability and quality.
Strategies for Capitalizing on Opportunities
To effectively capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable furniture, Southeast Asian exporters need to adopt a multi-pronged approach encompassing certifications, targeted marketing, and continuous innovation.
Obtaining relevant certifications (e.g., Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification for sustainably sourced wood) is crucial for building consumer trust and accessing specific markets. Targeted marketing campaigns that highlight the sustainability credentials of the products are essential to reach the environmentally conscious consumer segment. Continuous innovation in design, materials, and manufacturing processes will allow exporters to stay ahead of the competition and offer unique and desirable products.
Investing in research and development of new sustainable materials and technologies will further enhance their competitive edge.
The Future of Sustainable Furniture Exports from Southeast Asia
The burgeoning global demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products positions Southeast Asia advantageously for continued growth in furniture exports. This positive trajectory is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a growing preference for eco-friendly alternatives. However, navigating the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities within this evolving market requires strategic foresight and adaptation.The future of sustainable furniture exports from Southeast Asia hinges on several key factors, including evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and the region’s capacity to meet these demands sustainably.
Predicting the precise trajectory is complex, but several plausible scenarios emerge when considering these interwoven elements.
Global Demand Trends for Sustainable Furniture, Southeast Asian Furniture Exports Surge as Global Demand for Sustainable Materials Rises
Global demand for sustainable furniture is projected to experience robust growth in the coming years. Consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for products that align with their values, driving a shift towards materials like reclaimed wood, bamboo, and sustainably harvested rattan. This trend is amplified by stricter environmental regulations in key export markets, further incentivizing the adoption of sustainable practices.
For example, the European Union’s focus on circular economy principles is already impacting sourcing decisions for many furniture retailers, leading them to actively seek out suppliers who demonstrate robust sustainability credentials. This creates a strong pull effect for Southeast Asian exporters who can effectively demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices.
Potential for Further Growth in Southeast Asian Furniture Exports
Southeast Asia’s potential for further growth in sustainable furniture exports is significant. The region boasts abundant natural resources suitable for furniture production, a large and relatively low-cost labor pool, and a growing number of businesses adopting sustainable practices. However, realizing this potential requires addressing existing challenges, such as improving supply chain transparency and ensuring consistent quality control. Success will depend on the ability of Southeast Asian producers to scale their operations while maintaining their commitment to sustainability, ensuring a balance between economic growth and environmental responsibility.
Countries like Vietnam and Indonesia, with their established furniture industries and increasing focus on sustainable practices, are particularly well-positioned to benefit from this growth.
Technology and Innovation’s Role in Shaping the Future
Technology and innovation will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the Southeast Asian furniture export industry. Automation in manufacturing processes can improve efficiency and reduce waste, while advancements in material science could lead to the development of even more sustainable and durable alternatives. Digital technologies, such as blockchain, can enhance supply chain transparency, allowing consumers to trace the origin and journey of their furniture, building trust and promoting responsible sourcing.
Furthermore, the adoption of advanced design software can streamline the design process, minimizing material waste and optimizing production efficiency.
Future Scenarios: Positive and Negative Impacts
The future of Southeast Asian sustainable furniture exports presents a range of potential scenarios, both positive and negative:
- Positive Scenario 1: Sustainable Leadership: Southeast Asian nations proactively invest in sustainable forestry practices, implement stringent environmental regulations, and promote technological innovation. This leads to a significant increase in exports, creating high-value jobs and fostering economic growth while minimizing environmental impact. Examples include increased investment in reforestation projects and the development of innovative bio-based materials.
- Positive Scenario 2: Global Collaboration: International collaborations foster knowledge sharing and technology transfer, enabling Southeast Asian producers to adopt best practices in sustainable manufacturing and supply chain management. This leads to increased competitiveness and market access, driving sustainable growth across the region. An example would be joint ventures between European and Southeast Asian companies focused on sustainable design and production.
- Negative Scenario 1: Unsustainable Practices: A failure to address deforestation and unsustainable harvesting practices could lead to resource depletion, environmental damage, and reputational harm for the region. This could result in decreased demand for Southeast Asian furniture, hindering economic growth and potentially triggering international sanctions.
- Negative Scenario 2: Lack of Technological Adoption: A slow adoption of new technologies could hamper the region’s competitiveness, leading to a loss of market share to other regions with more advanced sustainable manufacturing capabilities. This would limit economic benefits and potentially cause job losses in the industry.
Closing Summary
Source: aimlandservices.com
The surge in Southeast Asian furniture exports, fueled by global demand for sustainable materials, signifies a positive shift towards environmentally and socially responsible consumption. While challenges remain, such as ensuring consistent supply chains and navigating international trade regulations, the opportunities for growth are substantial. By embracing innovation, investing in sustainable practices, and strategically marketing their products, Southeast Asian exporters can further capitalize on this trend, fostering economic growth while contributing to a more sustainable global furniture industry.
The future appears bright for this sector, with continued expansion expected as consumer awareness and demand for eco-friendly products continue to rise.
FAQs
What are the main environmental benefits of using sustainable materials in furniture production?
Sustainable materials reduce deforestation, minimize carbon emissions associated with manufacturing, and lessen the overall environmental impact compared to using unsustainable alternatives.
How do trade regulations affect Southeast Asian furniture exporters?
Trade regulations, including tariffs and import quotas, can impact export volumes and profitability. Navigating these regulations requires careful planning and adherence to international standards.
What are some innovative approaches being used in Southeast Asian furniture design?
Innovations include incorporating recycled materials, utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques for reduced waste, and developing unique designs that highlight the natural beauty of sustainable materials.
What role does certification play in the sustainable furniture market?
Certifications, such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and others, verify the sustainability of materials and production processes, enhancing consumer trust and market access.
What are the potential risks associated with this growth?
Risks include overexploitation of resources, potential price volatility of raw materials, and the need for continuous adaptation to evolving consumer preferences and market trends.
